Introduction📓
This is a pipeline that generates soundscape from street-level panoramic imagery (Google Streetview). The ability to simulate the sounds of various locations can enable immersive auditory experiences, with applications in virtual reality, geospatial navigation, environmental monitoring, and more. This pipeline provides a training-free framework composed of a VLM, a depth estimator, a grounding model, and a text-to-audio model to synthesize soundscape for the specified location.
Softwares Involve💻
- Programming languages: Python
- Tools: Pytorch, HuggingFace
- Models: InternVL2.5-MPO, Grounding DINO, DepthFM, TangoFlux
Project Demo
Below is the overview of the training-free framework:
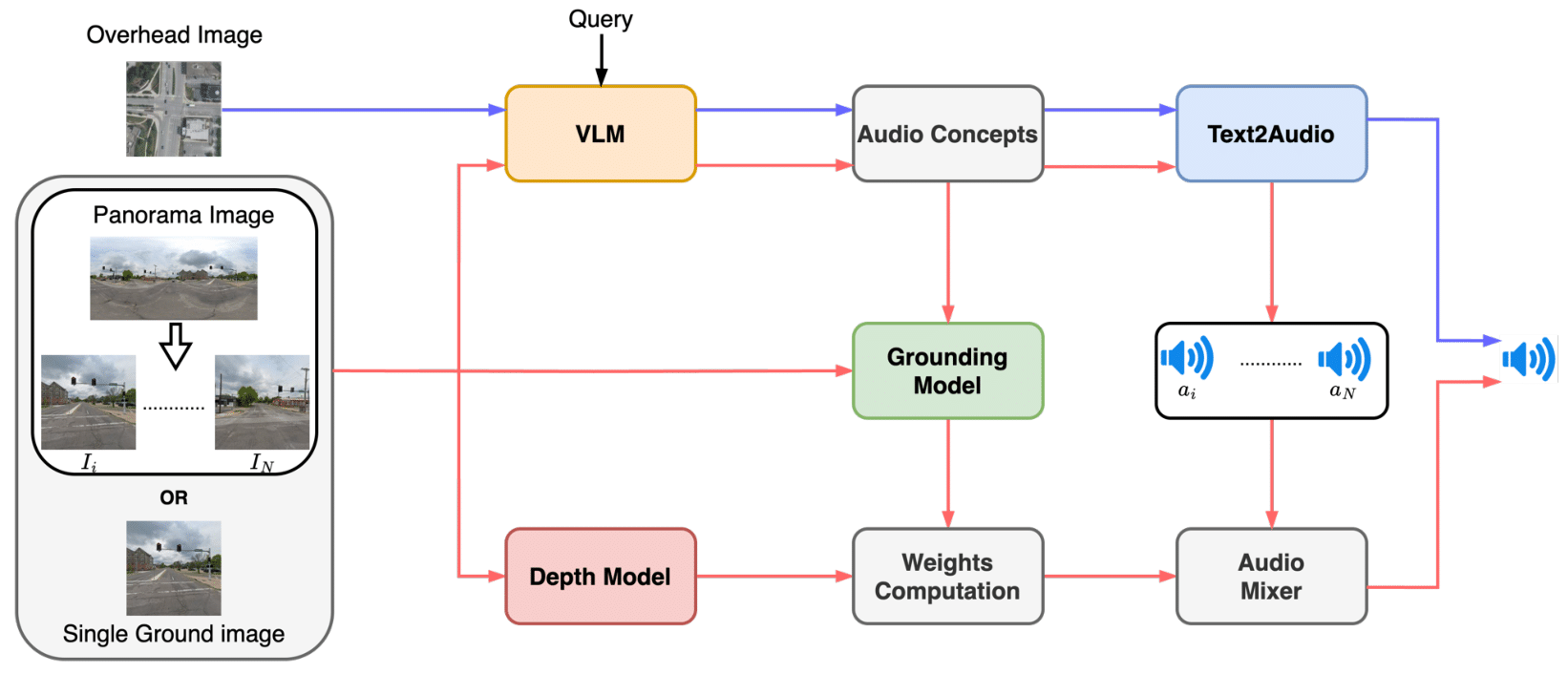
This framework synthesizes spatially aware soundscapes from ground-level imagery using a multi-stage pipeline. Starting with either a 360° panoramic image (split into N directional views) or a single ground-level image, we first employ a VLM to identify potential sound sources visible in the image.

A visual grounding model then precisely localizes these sound sources, while a monocular depth estimation model calculates their spatial positioning by estimating their distances from the viewer:


To determine a particular object’s distance from the camera, an image analysis algorithm is used to determine the pixel value within a bounding box given by the visual grounding model. And for each view, the pipeline finds the closest object to the view:

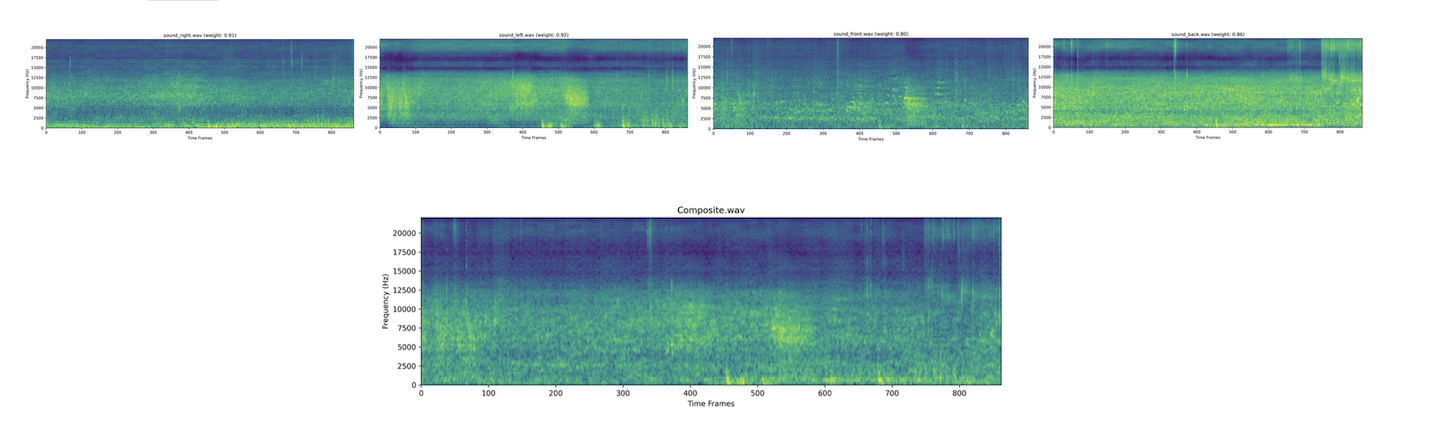
The pipeline uses TangoFlux to generate audios based on prompts. To simulate real-world audio propagation, we apply the inverse square law formulation. Based on the estimated distances of the audio sources, we select the top-m sound sources per image. For each identified sound source, a text-to-audio generative model synthesizes individual audio clips. In the final stage, spatial audio mixing adjusts the contribution of each sound source based on its distance—closer sources contribute more significantly to
the resulting soundscape.
References
Shilong Liu, Zhaoyang Zeng, Tianhe Ren, Feng Li, Hao Zhang, Jie Yang, Qing Jiang, Chunyuan Li, Jianwei Yang, Hang Su, et al. Grounding dino: Marrying dino with grounded pre-training for open-set object detection. In European Conference on Computer Vision, pages 38–55. Springer, 2024.
Ming Gui, Johannes Schusterbauer, Ulrich Prestel, Pingchuan Ma, Dmytro Kotovenko, Olga Grebenkova,Stefan Andreas Baumann, Vincent Tao Hu, and Bj¨orn Ommer. Depthfm: Fast monocular depth estimation with flow matching. arXiv preprint arXiv:2403.13788, 2024
Chia-Yu Hung, Navonil Majumder, Zhifeng Kong, Ambuj Mehrish, Rafael Valle, Bryan Catanzaro, and Soujanya Poria.Tangoflux: Super fast and faithful text to audio generation with flow matching and clap-ranked preference optimization. arXiv preprint arXiv:2412.21037, 2024