Introduction📓
This web calendar allows users to add, edit, and delete events. However, users must have an account to perform the aforementioned actions. To create an account, click the Login button and then the Sign Up button. Rest assured, all sensitive information is hashed! The calendar’s implementation emphasizes preventing SQL injection attacks and utilizing CSRF tokens. If you have reservations but still want to test the website, feel free to use a simple password or one you’d never use elsewhere :D
Softwares Involve💻
- Programming languages: HTML, CSS, JavaScript, PHP, JSON, and SQL
- Tools: Amazon Web Services (EC2 Instance) and MySQL
Project Description📋
Here is the login page:
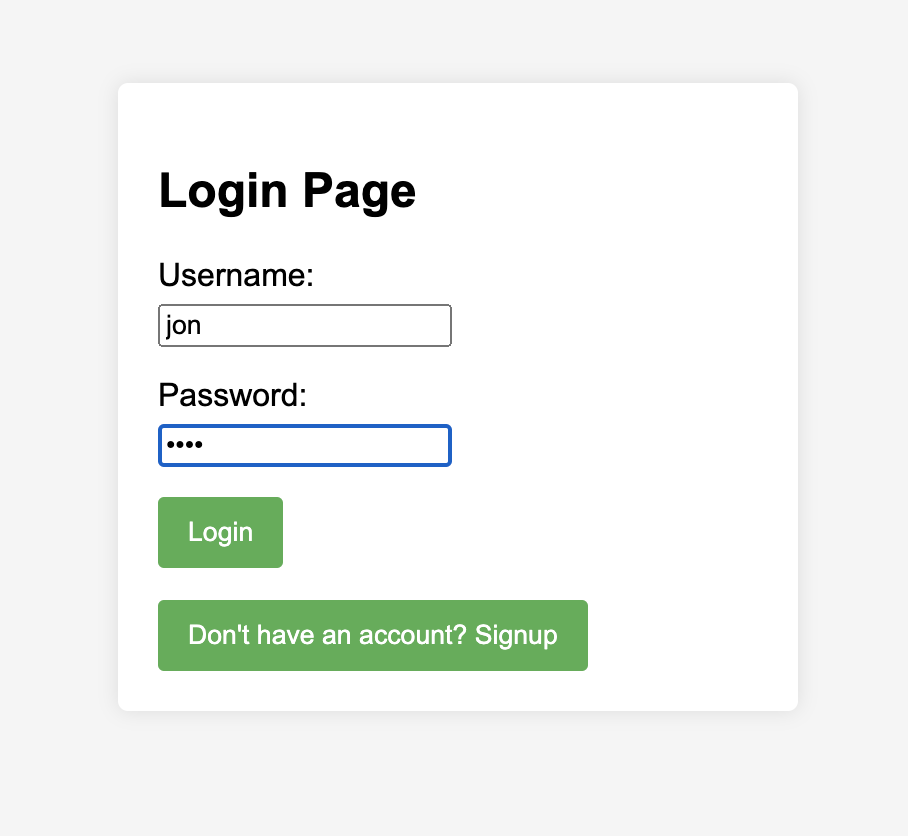
Users can create an account using the sign-up button. If a username already exists in the database, users will be prompted to choose a different one. As previously mentioned, all sensitive user data is hashed using PHP’s password_hash() function. The system also employs $stmt to both prevent SQL injections and enhance overall efficiency:
// Hash the password and store it in the database
$password = password_hash($password, PASSWORD_BCRYPT);
$stmt = $mysqli->prepare("INSERT INTO users (username, password) VALUES (?, ?)");
$stmt->bind_param('ss', $username, $password);
$stmt->execute();
$stmt->close();
The website also generates a CSRF token for each session to defend against CSRF attacks:
if (empty($_SESSION['csrf_token'])) {
$_SESSION['csrf_token'] = bin2hex(random_bytes(32));
}
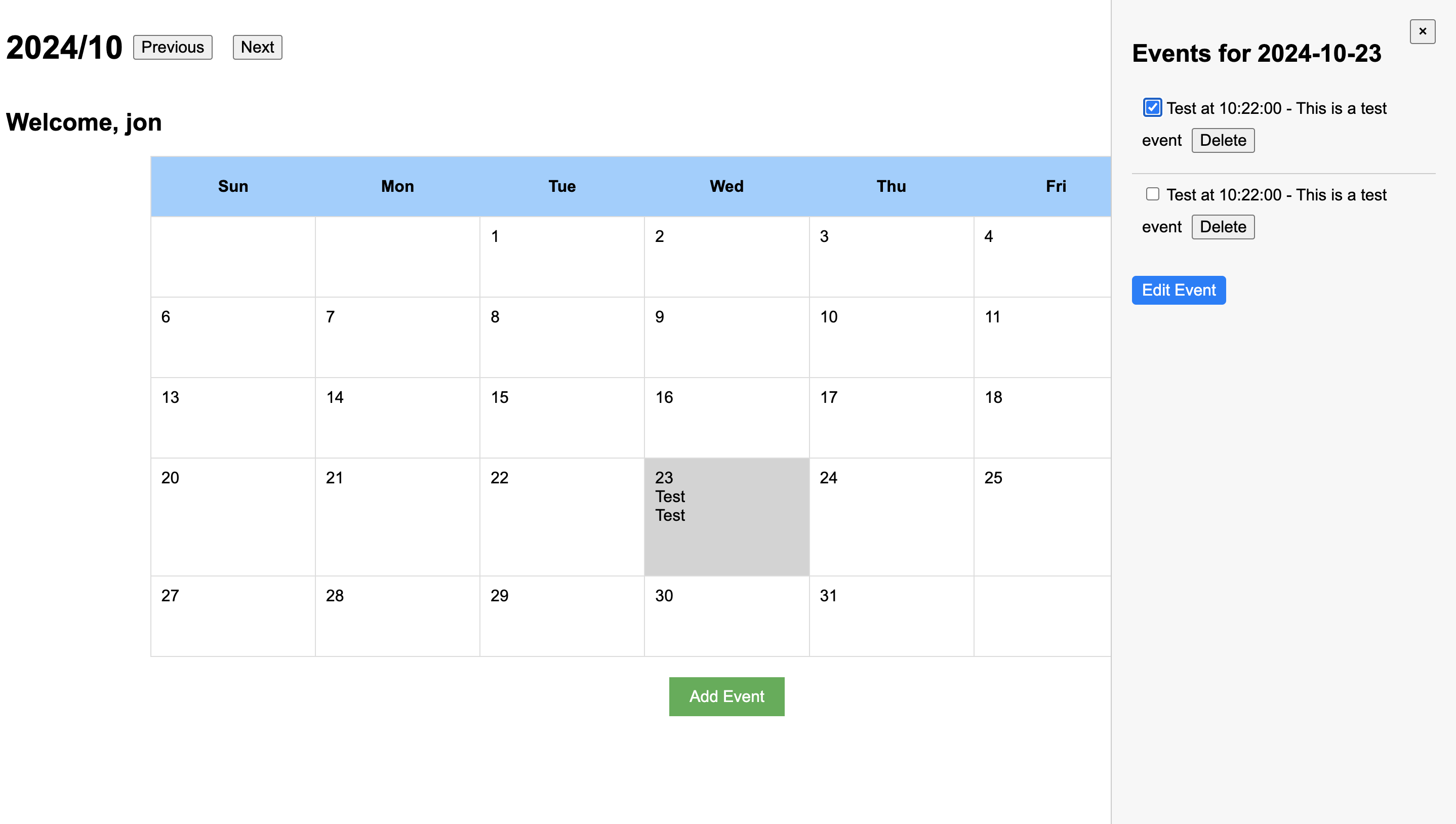
Once logged in, users can add events to the calendar:
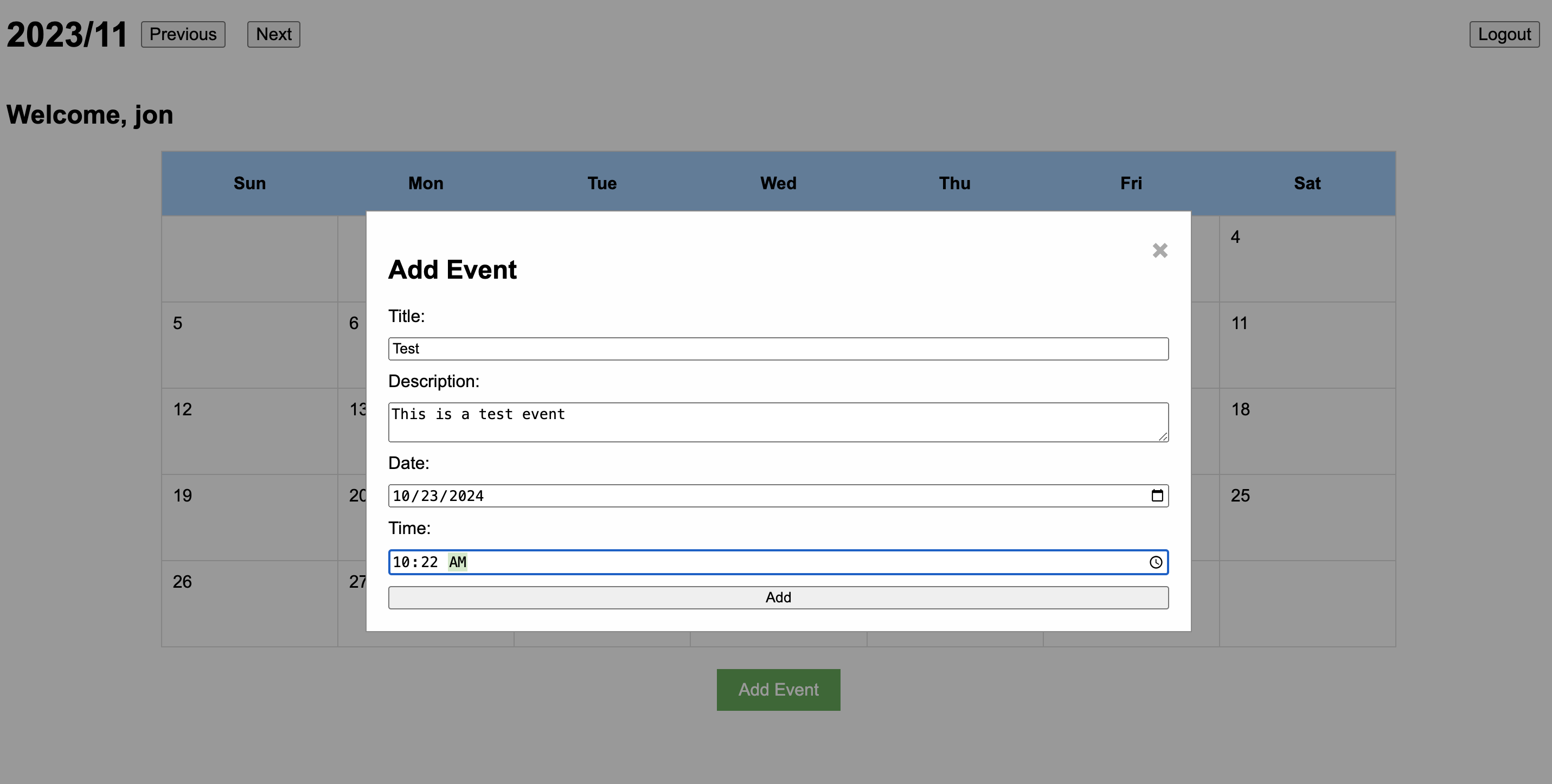
To facilitate this feature, the event addition process leverages AJAX and PHP for front-end to back-end communication. Here’s a snippet from add_event_ajax.php:
Snippet of add_event_ajax.php:
$stmt = $mysqli->prepare("INSERT INTO events (title, description, event_date, event_time, user_id) VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?, ?)");
if(!$stmt) {
echo json_encode(array("success" => false, "message" => $mysqli->error));
exit;
}
$stmt->bind_param('ssssi', $title, $description, $date, $time, $_SESSION['user_id']);
if($stmt->execute()) {
echo json_encode(array("success" => true));
} else {
echo json_encode(array("success" => false, "message" => "Error inserting event."));
}
Below is the JavaScript code that facilitates adding events to the database. It’s important to note that the data is transmitted in JSON format to the database:
fetch("add_event_ajax.php", {
method: 'POST',
body: JSON.stringify(eventData),
headers: { 'content-type': 'application/json' }
}).then(response => response.json())
.then(data => {
if (data.success) {
alert("Event added successfully!");
} else {
const errorMessage = document.getElementById("error-message");
errorMessage.textContent = data.message;
}
})
.catch(err => {
console.log(JSON.stringify(eventData));
console.error(err);
const errorMessage = document.getElementById("error-message");
if(errorMessage) {
errorMessage.textContent = err.message || "An unexpected error occurred.";
}
});
Users can also delete or edit an event. By clicking one of the cells on the calendar, users can call out an event sidebar that displays all the events on that day: